A key component of the power transmission system for automobiles is the Transmission Shaft. Its main purpose is to send the engine’s torque to the drive axle via the transmission (or transfer case), hence pushing the wheels to spin. To assist readers in better understanding this crucial component, this article will offer a thorough introduction to the Transmission Shaft, including its definition, structural composition, typical defects, maintenance, and more.
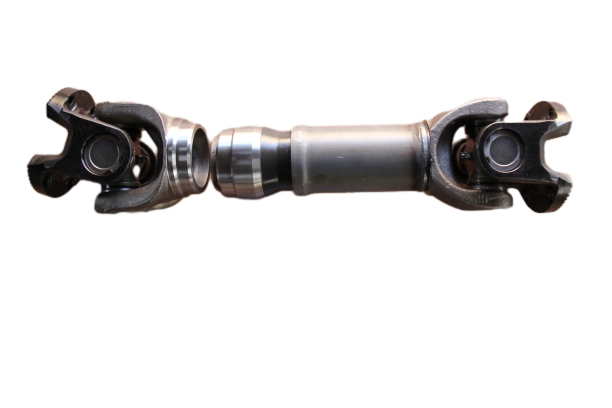

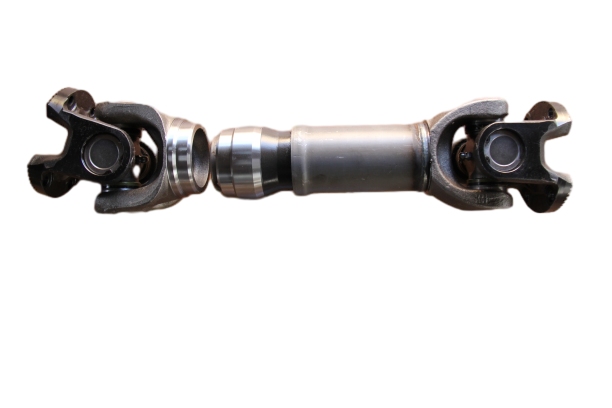
Volvo Transmission Shaft
1.Transmission Shaft: Definition and Function
Connecting the driving axle to the vehicle’s gearbox (or transfer case), the gearbox Shaft is a vital transmission component. Its major function is to precisely transfer the torque and speed, controlled by the transmission, to the drive axle, therefore supplying enough driving force to the wheels to attain smooth operation of the vehicle. Its design has to guarantee enough strength and toughness as the Transmission Shaft runs at high rotational speeds, as well as great dynamic balancing performance to avoid vibrations, noise, or early wear brought on by imbalance.
2.Transmission Shaft Classification and Structural Composition
The Transmission Shaft can be classified into two primary types—hollow and solid shafts—depending on the application and design criteria.
Hollow Shaft Transmission
Most cars have hollow shafts. Usually, these are created by welding consistent thickness thin steel plates. Hollow shafts have benefits such as lower total weight, better transmission efficiency, and less centrifugal force produced during high-speed rotation.
Shaft of Solid Transmission
Steering drive axles, split drive axles, and certain microcars all employ solid shafts. Made from one piece of metal, they provide more rigidity and lifetime under particular unique operating conditions.
Usually welded with spline shaft heads, the ends of the Transmission Shaft provide exact connection with the driving axle and transmission. A center support is usually fitted in the middle of the shaft to offset axial and angular changes brought on by chassis deformation or installation mistakes. The center support balances the stresses on the shaft and absorbs vibrations as well as maintains the segmented connection of the shaft.
Modern car transmission shafts also include universal joints—including cross shafts and needle bearings—which guarantee consistent power transmission even under angular change during operation, therefore ensuring reliable power transmission even when the car turns or travels difficult terrain.
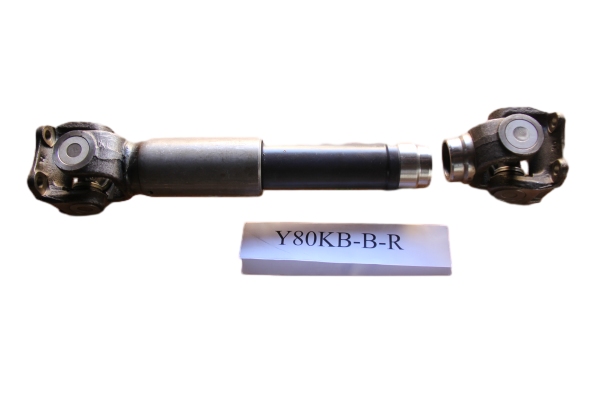

Isuzu Transmission Shaft
3. Working Principle of the Transmission Shaft in Automotive Power System
The functioning concept of the Transmission Shaft, a crucial link in the power transmission chain, can be stated as follows:
Power is produced by the engine; the transmission controls it and then outputs.
Its robust structure transmits the torque produced from the transmission to the drive axle.
The drive axle powers the wheels, hence propelling the car.
The transfer Shaft has to guarantee seamless torque transfer during this time while compensating for shocks and vibrations brought on by uneven road surfaces or changing vehicle speed. Thus, when constructing the Transmission Shaft, dynamic balancing, bending resistance, and fatigue resistance should all be taken into account.
4. Typical Faults and Diagnostic Techniques
The Transmission Shaft may suffer the following typical defects from extended high-speed operation and constant load changes:
4.1 Vibration and Wobble of the Transmission Shaft Fault Symptoms
Abnormal noise and noticeable vibration during start-up or low-speed driving; Increased vibration and noise when changing speed or moving gears.
Diagnostic Techniques: Measure the radial run-out of the Transmission Shaft using expert tools including dial indicators. A shaft could be bent or the balance weights might have fallen off if the run-out beyond the specified limit, often about 0.8 mm. Inspect the spline fit of the universal joint connections and the telescopic tube as well to avoid wear-related looseness.
4.2 Abnormal Noise from the Transmission Shaft Fault Symptoms
Unusual noise from the bottom of the vehicle whilst driving; Reduced wobble of the Transmission Shaft when the handbrake is engaged, with the noise coming back when released.
Diagnostic Techniques:
First, look for shaft bending or balance weight separation. Then check the universal joints, splines, and connecting nuts for wear or looseness that can be noisy. Universal joint cross shaft or needle bearing wear or damage calls for quick replacement.
4.3 Transmission Shaft Imbalance Fault Symptoms:
Imbalance causes the center of mass of the Transmission Shaft to drift from the rotating center, hence generating perceptible vibration at high speeds.
Diagnostic Techniques:Examine the shaft with a dynamic balance tester. Should the shaft be re-balanced or should balance weights be added to remove the eccentric force if notable imbalance is found?
5. Transmission Shaft Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance and periodic checks are absolutely necessary to guarantee the Transmission Shaft stays in good functioning order and to prolong its service life. Some of the suggested upkeep items below are:
5.1 Correct Driving Habits
Don’t begin in high gear. High gear start-up introduces the Transmission Shaft to a rapid, large torque impact, which might lead component wear.
Lift the clutch gently; sudden clutch lifting can create unequal shocks to the transmission system. Starting slowly and shifting gears gently is advised.
Stay away from speeding and overloading. Both overloading and speeding put more stress on the Transmission Shaft, which might reduce its lifetime if done often.
5.2 Routine Lubrication and Inspection
Look over connector parts: To guarantee no looseness, fractures, or wear, routinely inspect the tightness of the transmission shaft hanger, universal joints, splines, and support components.
Lubricate right away: Regular lubrication with appropriate grease is needed for the universal joints and cross bearings of the Transmission Shaft. To guarantee proper lubrication under varied temperatures, use several kinds of lithium-based grease depending on the season—Grade 3 in summer and Grade 2 in winter.
5.3Assembly and Disassembly Precautions
The following should be kept in mind when constructing a new Transmission Shaft or doing maintenance disassembly:
Mark assembly locations: Install with the indications on the telescopic sleeve in mind to guarantee the flange fork is in the same plane. During reassembly, avoid positional discrepancies.
Safely secure the car: Before taking apart the Transmission Shaft, make sure the front and rear wheels of the car are firmly fastened to avoid accidents.
Inspect and take apart in order: To make sure all indicators satisfy the criteria, take out the connecting parts in sequence and check the clearance of important components (e.g., the spline teeth and sliding fork should not exceed 0.4 mm).

Xinjiang Huai Transmission Shaft
6. Development Trends and Extended Knowledge of the Transmission Shaft
The design and manufacture of the Transmission Shaft are also always changing with the ongoing development of automobile technology. Some future development tendencies and extended knowledge points are as follows:
6.1 Structural Optimization and Material Upgrades
Usually, traditional transmission shafts consist of seamless steel tubes or steel plate welding. But new high-strength metals and composite materials are progressively being used in Transmission Shaft manufacture to provide a mix of lightweight and high strength. This not only greatly lowers the weight but also improves corrosion and wear resistance, hence prolonging the service life of the shaft.
6.2 Predictive Maintenance and Intelligent Monitoring
Modern cars are stressing intelligence more and more; the Transmission Shaft is not exception. Real-time monitoring of the working condition is possible by attaching vibration, temperature, and torque sensors on the shaft. By means of big data analysis, this enables the prompt identification of anomalies, early alerts, and the development of scientific maintenance plans, therefore attaining predictive maintenance and lowering maintenance costs and failure rates.
6.3 Dynamic Simulation and System Integration
The gearbox Shaft is intimately linked to parts like the gearbox, drive axle, and center support in the construction of the whole vehicle transmission system. The performance of each component under various operating situations can be predicted during the design phase by means of system integration and dynamic simulation technology, therefore optimizing the whole transmission solution. This combined design increases the stability and safety of the whole car as well as the efficiency of transmission.
6.4Trends in Energy Efficiency and Environmental Protection
The automotive sector is always investigating environmentally friendly technology given the rising worldwide need for energy conservation and pollution reduction. The Transmission Shaft’s lightweight construction not only lowers greenhouse gas emissions but also helps to cut car fuel use. The evolution of Transmission Shaft technology will be opened in the future by the synergy of energy-saving lubricants and eco-friendly production techniques.

FAW Jiefang Transmission Shaft
7.Final thoughts
In the vehicle transmission system, the Transmission Shaft is quite important. Structurally, it is made up of hollow or solid shafts, spline shaft heads, universal joints, and center supports. Functionally, its major duty is to guarantee that the output torque of the engine is delivered stably and efficiently to the drive axle, which subsequently distributes the power to the wheels to achieve the vehicle’s power transmission. Though the Transmission Shaft is susceptible to problems including bending, vibration, and wear during high-speed operation, rational design, routine maintenance, and scientific repair can help to address these concerns.
Furthermore, the production process and performance of the Transmission Shaft are always getting better with the evolution of material technology, smart detecting technology, and system integration design. The Transmission Shaft is changing from conventional steel shafts to future high-molecular composite material goods in lightweight, high-strength, environmentally friendly, and smart directions, thereby strongly supporting the general performance enhancement of cars.
All things considered, knowing the fundamental information and maintenance aspects of the automotive Transmission Shaft not only enables maintenance professionals to swiftly identify problem causes but also enables car owners to better appreciate this vital component of their cars. The safety and stability of the vehicle during driving can only be guaranteed by paying attention to meticulous control at every level, hence enabling a more comfortable and dependable driving experience for drivers.

